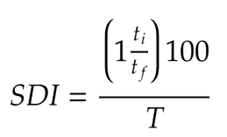
What Measurements Determine Feed Water Suitability for Reverse Osmosis?
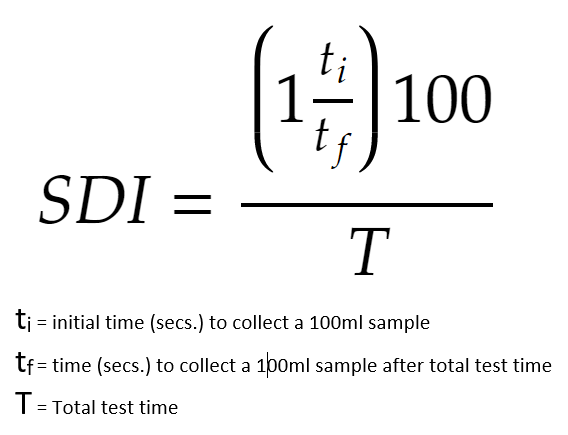
SDI (Silt Density Index) is a measure of the turbidity or cloudiness of water, and it is used as a performance indicator for reverse osmosis (RO) systems. The SDI of water is determined by measuring the rate at which a suspension of fine particles settles in a standard container over a specific time period.
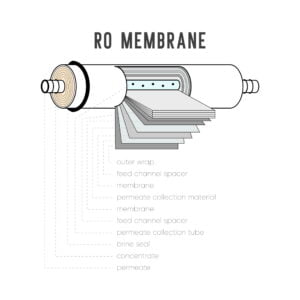
In general, the lower the SDI value, the clearer and cleaner the water is. The SDI limit for reverse osmosis systems is typically set at a maximum value of 5 or less, although some systems may have lower limits. This limit is important because higher SDI values can indicate the presence of high levels of suspended solids, which can clog or foul the RO membranes and reduce the efficiency of the system.
SDI measuring equipment can be purchased to perform the this test. The SDI testing kit comprises of a measuring glass >100ml, pressure adjustment valve to adjust to 30 PSI for the test, pressure gauge and filter housing to place a 0.45 micrometre filter pad.
To perform the test, set up and flush the equipment, and set the pressure to 30 PSI (2.1 bar).
Isolate the flow then place the filter pad in the housing, using a stop watch measure how long it takes to fill the measuring glass to 100ml and record the initial time. Continue to let water to flow through the the filter for 15 minutes then take another measurement and time how long it takes to fill the measuring glass to 100ml, measure the time.
Using the formula calculate the SDI.