Understanding Bio-Fouling: Causes, Effects, and Prevention
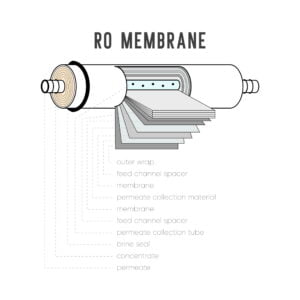
Biofouling is the accumulation of microorganisms, such as bacteria, algae, and fungi, on the surface of reverse osmosis (RO) membranes, which can negatively impact the performance and efficiency of the RO system. To prevent biofouling, it’s important to implement proper maintenance and cleaning procedures, as well as to incorporate additional pre-treatment steps into the RO process.
Here are some common methods for preventing biofouling on RO membranes:
- Chemical Cleaning: Regular cleaning with biocides, such as chlorine or hydrogen peroxide, can kill microorganisms and prevent the formation of biofilms on the RO membranes.
- Physical Cleaning: Physical cleaning methods, such as high-pressure backwashing or ultrasonic cleaning, can help to remove biofouling from the RO membranes.
- Pre-Treatment: Pre-treatment steps, such as filtration or ultraviolet (UV) disinfection, can help to reduce the amount of microorganisms in the feedwater, thus reducing the potential for biofouling on the RO membranes.
- Proper Membrane Selection: Selecting RO membranes that are less susceptible to biofouling, such as those with a hydrophilic surface or a porous structure, can also help to prevent biofouling.
- Operating Conditions: Maintaining proper operating conditions, such as appropriate feed water temperature, pH, and pressure, can also help to reduce the risk of biofouling.
It’s important to regularly monitor the RO system for signs of biofouling and to implement corrective measures promptly to prevent significant damage to the RO membranes. Regular cleaning and maintenance, along with proper pre-treatment and operating conditions, can help to keep biofouling under control and ensure optimal performance of the RO system.