Optimizing Reverse Osmosis Antiscalant Dosage: Analyzing Dosing Ranges
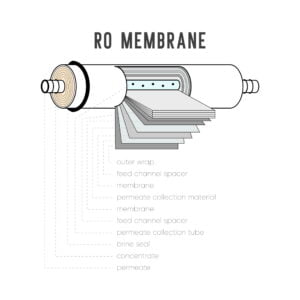
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a widely used water treatment process that involves the use of a semi-permeable membrane to remove impurities and particles from water. Antiscalants are an essential component of the reverse osmosis process, as they help prevent the build-up of scale and other deposits that can damage the membrane and reduce its efficiency. However, determining the optimal antiscalant dosage can be a challenging task, as it involves balancing the need for effective scale prevention with the potential for increased operating costs. In this article, we will examine the process of analyzing antiscalant dosage ranges and optimizing reverse osmosis performance.
Analyzing Antiscalant Dosage Ranges
The first step in optimizing antiscalant dosage is to analyze the dosage ranges that are currently being used. This involves monitoring the system’s performance and testing the effectiveness of the antiscalants at different dosages. By collecting data on the system’s performance and the amount of antiscalant used, it is possible to determine the optimal dosage range for a given system. This information can then be used to adjust the dosage to achieve the best results with the lowest possible cost.
It is important to note that the optimal dosage range for a particular system will depend on a variety of factors, including the type and quality of the feed water, the type and age of the membrane, and the operating conditions of the system. It may be necessary to adjust the dosage range over time as these factors change. Additionally, it is important to consider other factors that can affect the performance of the system, such as temperature, pressure, and flow rate.
Optimizing Reverse Osmosis Performance
Once the optimal antiscalant dosage range has been determined, it is important to take steps to optimize the performance of the reverse osmosis system. This may involve adjusting other aspects of the system, such as the pH level of the feed water or the flow rate of the water through the membrane. It may also involve making changes to the antiscalant treatment process, such as the frequency of dosing or the type of antiscalant used. The typical antiscalant dosing range is between 0.5 and 4 mg/L
In addition to optimizing the performance of the system, it is important to monitor the system on an ongoing basis to ensure that it is operating efficiently and effectively. This may involve regular testing of the feed water and product water, as well as monitoring the pressure and flow rates throughout the system. By regularly monitoring the system and making adjustments as necessary, it is possible to maintain optimal performance and extend the life of the membrane.
Optimizing the antiscalant dosage range is an important part of maintaining the performance and efficiency of a reverse osmosis system. By carefully analyzing the dosage range and monitoring the system’s performance, it is possible to achieve effective scale prevention while minimizing operating costs. Additionally, by taking steps to optimize the overall performance of the system and monitoring it on an ongoing basis, it is possible to extend the life of the membrane and ensure the long-term success of the RO process.