Reverse Osmosis: Tracing the Evolution of a Water Treatment Method
Water is an essential resource for life, and over the years, humans have developed various techniques to ensure that it is clean and safe for consumption. One of the most popular methods of water treatment today is reverse osmosis. This technology has undergone significant advancements since its inception, making it even more efficient and effective. In this article, we will explore the history and evolution of reverse osmosis.
The Origins of Reverse Osmosis: A Brief History
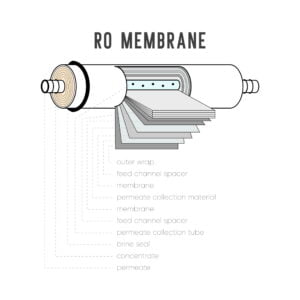
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water treatment technology that was developed in the late 1950s. The concept of osmosis was first studied by a French physicist named Jean-Antoine Nollet in 1748. It wasn’t until the 1950s that researchers discovered that by applying pressure to the water on the other side of the membrane, water molecules could be forced through the membrane, leaving behind impurities.
The first commercial RO plant was installed in the United States in 1965, and since then, the technology has continued to evolve. In the 1970s, thin film composite (TFC) membranes were developed, which greatly improved the efficiency of RO systems. Later, in the 1990s, spiral-wound membranes were introduced, which reduced the size and cost of RO systems.
Advancements in Reverse Osmosis Technology: Today and Beyond
Today, RO technology has advanced even further, making it more efficient and cost-effective than ever before. One of the most significant advancements in recent years is the development of high-rejection membranes. These membranes are capable of removing up to 99.9% of all contaminants, including viruses and bacteria. This has made RO systems an excellent choice for a variety of applications, including industrial and municipal water treatment.
Another significant advancement in RO technology is the development of energy-efficient systems. These systems use less electricity to operate than traditional RO systems, making them more environmentally friendly and cost-effective in the long run. Some manufacturers are even exploring the use of renewable energy sources to power RO systems, further reducing their environmental impact.
In conclusion, reverse osmosis is a water treatment technology that has come a long way since its inception in the 1950s. Advancements in membrane technology and system design have made RO systems more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly than ever before. As the demand for clean, safe water continues to grow, it’s likely that we’ll see even more innovation in RO technology in the years to come.