Removing Phosphate From Wastewater
Removing phosphate from wastewater is an important step in wastewater treatment to prevent water pollution and protect aquatic ecosystems. Here are some commonly used methods for phosphate removal:
- Chemical Precipitation: a. Coagulation and Flocculation: Add coagulants such as aluminum sulfate (alum) or ferric chloride to wastewater. These chemicals form insoluble precipitates with phosphate ions, which can then be removed through sedimentation or filtration. b. Lime Softening: Adjust the pH of the wastewater by adding lime (calcium hydroxide). This process promotes the formation of calcium phosphate precipitates, which can be separated from the water.
- Biological Treatment: a. Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal (EBPR): Utilize specific bacteria that can accumulate phosphate as intracellular polyphosphate. In this process, the wastewater is treated in an anaerobic and aerobic environment, promoting the growth of these bacteria and subsequent removal of phosphate.
- Adsorption: a. Adsorbent Materials: Use adsorbent materials like activated carbon, activated alumina, or iron oxide to capture phosphate ions from wastewater. The adsorption process relies on the surface properties of these materials to attract and bind phosphate.
- Ion Exchange: a. Ion Exchange Resins: Employ ion exchange resins that have a high affinity for phosphate ions. The resin exchanges phosphate ions in the wastewater with other ions, effectively removing phosphate from the water.
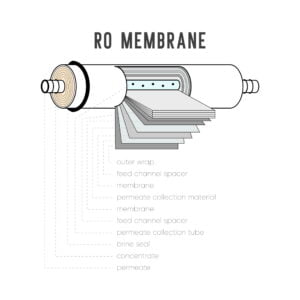
- Membrane Technologies: a. Reverse Osmosis (RO): Use a semipermeable membrane to separate phosphate ions and other contaminants from water through a pressure-driven process. RO is highly effective in removing phosphate but can be energy-intensive and generate concentrated brine waste. b. Nanofiltration (NF) or Ultrafiltration (UF): These membrane filtration processes can selectively remove phosphate ions based on their molecular size, effectively reducing phosphate concentrations in the treated water.
- Electrocoagulation: a. Apply an electrical current to the wastewater, causing the formation of metal hydroxide precipitates. These precipitates adsorb and trap phosphate ions, allowing their removal by sedimentation or filtration.
It’s important to note that the most suitable phosphate removal method depends on factors such as the initial concentration of phosphate, the desired level of removal, available resources, and specific wastewater treatment goals. A combination of methods may be employed in wastewater treatment plants to achieve optimal phosphate removal efficiency.